Freeform Shading and Lighting Systems from Planar Quads
 By Caigui Jiang
By Caigui Jiang
Abstract
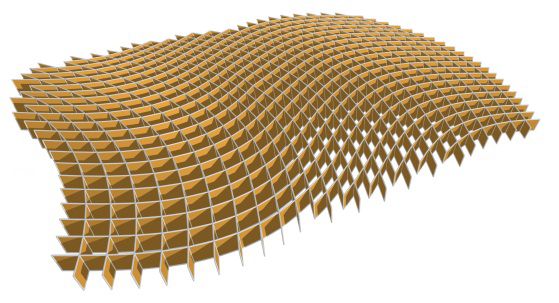
The topic of this paper is optimized shading and lighting systems which consist of planar fins arranged along the edges of a quad-dominant base mesh, that mesh itself covering a reference surface. Such an arrangement can be observed e.g. in the Kogod courtyard roof designed by Foster / Partners for the National Portrait Gallery in Washington DC (Fig. 1). A reference surface consisting of three vaults with curved valleys in between is panelized by a quad mesh whose faces are not planar; planar glass panels are mounted on a grid of quadrilateral fins which follow the edges of the quad mesh. In our paper we consider structures of exactly that type, whose geometry is hierarchically set up as follows,The first element in the hierarchy is the reference surface, which may be any freeform shape. Secondly, the reference surface is panelized by a quad-dominant mesh, which is referred to as the base mesh. Thirdly, planar fins are arranged along the edges of the base mesh such that in each vertex the planes of fins nicely intersect in a common node axis.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.