Freeform Quad-based Kirigami
 By Caigui Jiang
By Caigui Jiang
Abstract
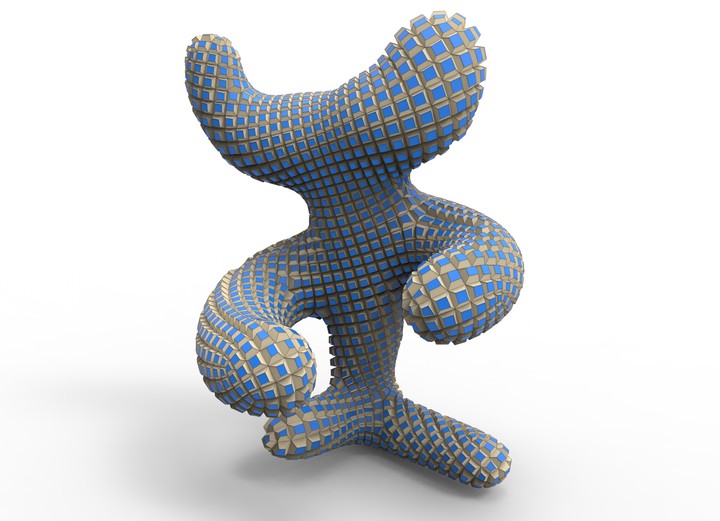
Kirigami, the traditional Japanese art of paper cutting and folding generalizes origami and has initiated new research in material science as well as graphics. In this paper we use its capabilities to perform geometric modeling with corrugated surface representations possessing an isometric unfolding into a planar domain after appropriate cuts are made. We initialize our box-based kirigami structures from orthogonal networks of curves, compute a irst approximation of their unfolding via mappings between meshes, and complete the process by global optimization. Besides the modeling capabilities we also study the interesting geometry of special kirigami structures from the theoretical side. This experimental paper strives to relate unfoldable checkerboard arrangements of boxes to principal meshes, to the transformation theory of discrete diferential geometry, and to a version of the Gauss theorema egregium.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.